How to Implement SSR in Next.js: Complete Guide
Learn how to implement SSR in Next.js with this 2025 guide. Boost SEO, speed, and Google rankings with our step-by-step Next.js SSR tutorial.
When building applications, developers often start with a monolithic architecture, where all features are developed and deployed within a single project. While this approach is suitable for small applications, it becomes challenging to maintain, scale, and deploy as the application grows. To overcome these limitations, modern applications use microservices architecture, where the system is broken into smaller, independent services that can be developed and scaled separately. NestJS, a powerful and progressive Node.js framework built with TypeScript, offers first-class support for building microservices. It supports multiple communication transports such as TCP, Redis, MQTT, NATS, Kafka, and gRPC, making it an excellent choice for building scalable, distributed, and high-performance microservices. In this blog, we will explore what microservices are, why to use microservices, and how to implement microservices in NestJS step by step.
A microservice is a small, independent application designed to perform one specific business function. Instead of building a single large application, the system is divided into multiple focused services, each responsible for a particular task.
Each microservice:
Runs independently without affecting other services
Contains its own business logic and codebase
Communicates with other services using APIs or messaging protocols
This architecture improves scalability, maintainability, and fault isolation, making it ideal for modern distributed applications.
Understanding the difference between Monolithic Architecture and Microservices Architecture is essential when designing scalable applications.
A monolithic application is built as a single, large project where all features are tightly coupled.
Key Characteristics:
Single large codebase
All features live in one application
If one component fails, it can impact the entire system
Difficult to scale and maintain as the application grows
A microservices-based application is composed of multiple small, independent services, each handling a specific responsibility.
Key Characteristics:
Multiple small, independent services
Each service has a single responsibility
Services can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently
Easier to maintain and extend over time
Choosing microservices improves scalability, flexibility, and deployment speed, especially for large and growing applications.
NestJS is an excellent choice for microservices because:
Built-in microservices module
Supports multiple transport layers
Strong TypeScript support
Modular and scalable architecture
Clean and structured code
Easy to learn if you know basic JavaScript
Inspired by Angular (great for enterprise apps)
NestJS allows services to talk to each other using messages instead of HTTP routes.
A typical NestJS microservices setup includes:
API Gateway (optional)
Client Service – sends messages
Microservice – listens and responds
Transport Layer – Kafka/gRPC /Redis/MQTT etc.
API Gateway → Message → Microservice → Response
NestJS uses message patterns instead of REST routes for communication.
We will create four applications:
npm i -g @nestjs/cli
Choose npm or yarn and enable TypeScript.
1. 3 Microservices
2. API Gateway – Client
#1 nest new user-service
#2 nest new order-service
#3 nest new payment-service
#4 nest new api-gateway
Now we have four separate applications.
Open user-service/src/main.ts
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
import { MicroserviceOptions, Transport } from '@nestjs/microservices';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.createMicroservice(
AppModule,
{
transport: Transport.TCP,
options: {
host: '127.0.0.1',
port: 3001,
},
},
);
await app.listen();
}
bootstrap();
Open user-service/src/app.controller.ts
import { Controller } from '@nestjs/common';
import { MessagePattern } from '@nestjs/microservices';
@Controller()
export class AppController {
@MessagePattern({ cmd: 'get_users' })
getUsers() {
return [
{ id: 1, name: 'Amit' },
{ id: 2, name: 'Rahul' },
];
}
}
Here,@MessagePattern works like a route, but for messages.
Open order-service/src/main.ts
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
import { MicroserviceOptions, Transport } from '@nestjs/microservices';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.createMicroservice<MicroserviceOptions>(
AppModule,
{
transport: Transport.TCP,
options: {
host: '127.0.0.1',
port: 3002,
},
},
);
await app.listen();
}
bootstrap(); Open order-service/src/app.controller.ts
import { Controller } from '@nestjs/common';
import { MessagePattern } from '@nestjs/microservices';
@Controller()
export class AppController {
@MessagePattern({ cmd: 'get_orders' })
getOrders() {
return [
{ id: 1, item: 'Laptop' },
{ id: 2, item: 'Phone' },
];
}
}
Order Service listens on port 3002 and handles order-related data.
Open payment-service/src/main.ts
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
import { MicroserviceOptions, Transport } from '@nestjs/microservices';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.createMicroservice(
AppModule,
{
transport: Transport.TCP,
options: {
host: '127.0.0.1',
port: 3003,
},
},
);
await app.listen();
}
bootstrap();
Open payment-service/src/app.controller.ts
import { Controller } from '@nestjs/common';
import { MessagePattern } from '@nestjs/microservices';
@Controller()
export class AppController {
@MessagePattern({ cmd: 'get_payments' })
getPayments() {
return [
{ id: 1, amount: 5000, status: 'SUCCESS' },
{ id: 2, amount: 2000, status: 'PENDING' },
];
}
}
Payment Service listens on port 3003 and manages payment-related data.
npm install @nestjs/microservices
Open api-gateway/src/app.module.ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ClientsModule, Transport } from '@nestjs/microservices';
import { AppController } from './app.controller';
@Module({
imports: [
ClientsModule.register([
{
name: 'USER_SERVICE',
transport: Transport.TCP,
options: { host: '127.0.0.1', port: 3001 },
},
{
name: 'ORDER_SERVICE',
transport: Transport.TCP,
options: { host: '127.0.0.1', port: 3002 },
},
{
name: 'PAYMENT_SERVICE',
transport: Transport.TCP,
options: { host: '127.0.0.1', port: 3003 },
},
]),
],
controllers: [AppController],
})
export class AppModule {}
Open api-gateway/src/app.controller.ts
import { Controller, Get, Inject } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ClientProxy } from '@nestjs/microservices';
import { firstValueFrom } from 'rxjs';
@Controller()
export class AppController {
constructor(
@Inject('USER_SERVICE') private userService: ClientProxy,
@Inject('ORDER_SERVICE') private orderService: ClientProxy,
@Inject('PAYMENT_SERVICE') private paymentService: ClientProxy,
) {}
@Get('users')
getUsers() {
return firstValueFrom(
this.userService.send({ cmd: 'get_users' }, {}),
);
}
@Get('orders')
getOrders() {
return firstValueFrom(
this.orderService.send({ cmd: 'get_orders' }, {}),
);
}
@Get('payments')
getPayments() {
return firstValueFrom(
this.paymentService.send({ cmd: 'get_payments' }, {}),
);
}
}
Here, This sends a message instead of calling an API directly.
# terminal 1
cd user-service
npm run start
# terminal 2
cd order-service
npm run start
# terminal 3
cd payment-service
npm run start
# terminal 4
cd api-gateway
npm run start
http://localhost:3000/users
http://localhost:3000/orders
http://localhost:3000/payments
Now you will see user data coming from the microservice, like
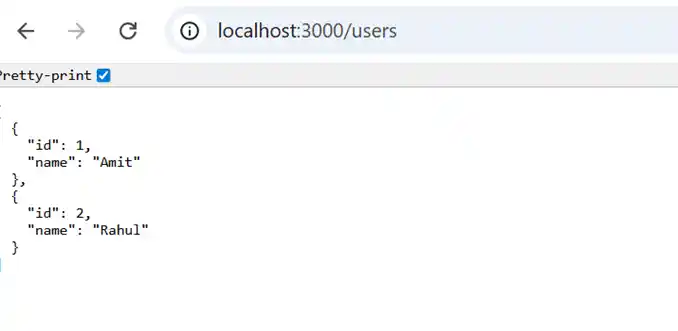
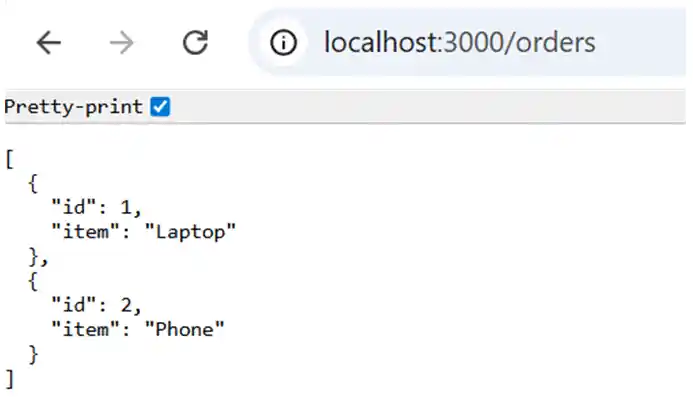
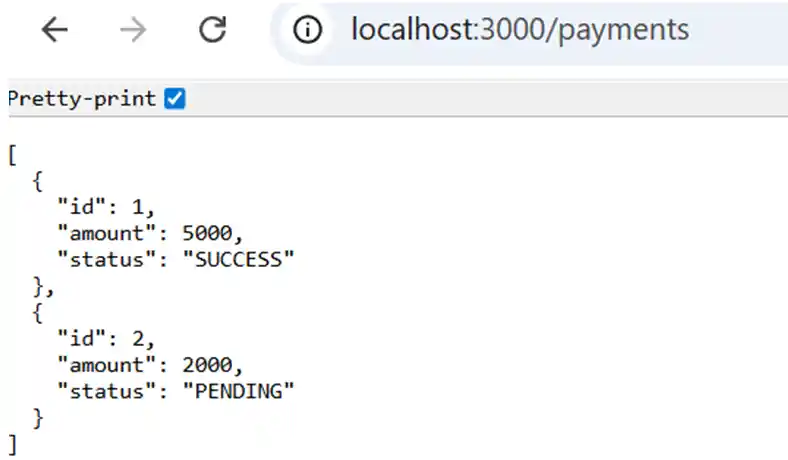
NestJS supports multiple transports:
TCP (default, simple)
Redis
MQTT
NATS
Kafka
gRPC
Choose based on scalability and reliability needs.
Use API Gateway pattern
Handle timeouts & retries
Implement logging & monitoring
Secure communication (JWT / mTLS)
Keep services small & focused
Use shared DTOs via libraries
Use microservices when:
Application is large and complex
Teams work independently
Need high scalability
Avoid microservices for small or simple applications.
NestJS makes implementing microservices simple and structured. With built-in support for messaging, transport layers, and dependency injection, it’s an excellent framework for building scalable distributed systems.
This example used TCP transport, but you can easily extend it to Redis, Kafka, MQTT or gRPC for production-grade systems.
Need expert help with NestJS, microservices architecture, or full-stack development? Prishusoft delivers reliable, scalable, and cost-effective software solutions. Contact us today to start building your next product with confidence.
Learn how to implement SSR in Next.js with this 2025 guide. Boost SEO, speed, and Google rankings with our step-by-step Next.js SSR tutorial.
Discover how to harness the power of Supabase with Next.js to create modern, scalable web applications. Learn to set up seamless backend and frontend integration, making your next project faster and more efficient.
Learn how to build an Electron desktop app with Next.js without using Nextron. Step-by-step tutorial with setup, scripts, and code examples for creating a cross-platform desktop app.
Learn how to build a CRUD GraphQL API with Next.js App Router using only the official GraphQL package. Step-by-step guide with schema, resolvers & UI.
Get in touch with Prishusoft – your trusted partner for custom software development. Whether you need a powerful web application or a sleek mobile app, our expert team is here to turn your ideas into reality.
